Is There A Link Between High Blood Pressure And Dementia?

June 26, 2025 by Robert Dowling | Fact Checked by Karen | Medically Reviewed by Dr. Bruce
Are you aware of your blood pressure reading? Has your blood pressure been monitored in recent years? High blood pressure increases the risk of heart attack and stroke. High blood pressure can exist without causing any symptoms, which is why it’s critical to get your blood pressure taken on a regular basis. Even if your blood pressure is in the normal range now, you need to do everything possible to maintain it there.
Blood Pressure: An Overview

The level of pressure exerted on the artery walls by blood vessels is referred to as blood pressure. The usual pressure should be between 120 and 80 mmHg. High blood pressure, on the other hand, occurs when this value rises at a rapid rate and can have life-threatening effects. When caused by a bad habit, high blood pressure can make the symptoms of many illnesses worse and make them last longer.
It can also be lethal if neglected for a long time. High blood pressure has been associated with a variety of illnesses, including dementia. Dementia is a condition that causes memory and cognitive functions to deteriorate. It can make it difficult to complete numerous duties and generate a lot of stress for both the person who has it and their career. Continue reading if you’re curious to see if there’s any evidence backing up this theory.
What Do The Experts Have To Say?
Several studies have found that there is a link involving high blood pressure and dementia. In the 2014 World Alzheimer’s Report, it was discovered that those between the ages of 15 and 40 who had high blood pressure had a higher risk of developing vascular dementia later in life. When someone has vascular dementia, their blood flow to the brain slows down. This means that the brain doesn’t get as much fuel to do its work.
Because high blood pressure causes blood vessels to narrow, it creates a barrier to the uninterrupted delivery of blood to numerous essential systems, including but not restricted to the brain. Even though there seems to be some link between the two, there is no real statistical data that proves the link.
The Effects Of High Blood Pressure On Brain Function
When you have high blood pressure, your arteries are restricted, as previously stated. The huge strain that such blood vessels are subjected to forces them to thicken and stiffen, resulting in blockages between them. Fats which pass through the blood tend to collect within these blockages, slowing the blood flow. If the arteries in the brain contract, the brain lacks essential nutrients like oxygen and blood; causing it to malfunction. High blood pressure may cause strokes, the most frequent of which is ischemic stroke.
Strokes can be caused by arterial thickening or artery rupture, resulting in brain bleeding. Both of these factors play a significant role in the development of vascular dementia. This bleeding can, in fact, happen without anyone noticing. Over time, the number of bleeds can build up, making it harder to do things and contributing to sub cortical vascular dementia.
Reading: What are the sings that you need probiotics?
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Blood Pressure Level
You may increase your chance of high blood pressure by growing older, developing diabetes, or if you have a family history of diabetes, but you can also battle it. This is how:
Reduce your Weight
It’s impossible to deny that as we gain weight, our blood pressure rises.Overweight people are more likely to get diabetes and heart disease. Even if you lose 10 pounds, your blood pressure will begin to drop.
Regular Exercise
One of the reasons exercise is so good at lowering blood pressure is that it causes your body to generate nitric acid. Blood vessels dilate as a result of nitric acid, lowering blood pressure. Exercise can also help you lose weight by strengthening your heart muscles and reducing stress.
Healthy Eating
Eating the appropriate kinds of food can help you avoid high blood pressure or get your blood pressure back to normal. Clinical trials have proven that a diet rich in fruits, veggies, low-fat dairy, chicken, whole grains, fish, and nuts is effective. You should also restrict fat, red meat, and too much sugar.
Break your salt addiction
Your body only requires about 500 milligrams of salt per day, yet the average person consumes up to 9,000 milligrams per day. Elevated salt levels have been linked to high blood pressure in studies. The current advice is to limit salt consumption to 2,400 milligrams per day, or roughly one teaspoon.
Smoking and drinking should be prohibited
If you want to keep your blood pressure in a healthy range, you should stop doing these two bad things.Alcohol increases blood pressure while also providing empty calories. A recommended quantity of alcohol for women is one drink per day, and two drinks per day for males. Smoking is harmful in any quantity. Nicotine constricts blood vessels, which elevates blood pressure. Quitting smoking lowers your chances of developing cancer or heart disease.
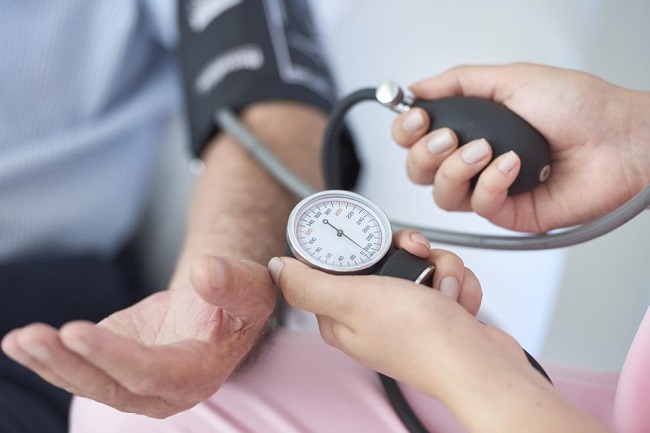
Keep track of your blood pressure level from time to time
A blood pressure reading by a competent healthcare expert is the only method to ascertain whether you have elevated or healthy blood pressure. A blood pressure reading should be taken at least every two years. Don’t take your normal blood pressure lightly if you recently had a blood pressure reading. Keep in mind that hypertension is a prevalent and often silent killer. Get off of the laptop, stop watching TV, get moving, have your fruits and veggies, and break any negative habits you have.
Final Verdict:
Although there is no definitive confirmation of a direct connection linking high blood pressure with dementia, it is obvious that the two are linked. High blood pressure causes the blood vessels to function harder than normal, causing them to burn out just like us. This would result in a deficiency of nutrients for the brain, which is the core risk factor for dementia due to decreased functionality. Maintaining regular blood pressure is among the best methods of keeping your brain healthy.
Up Next: How does diabetes impact sleep?